Cross Flow Water Turbine Design Manual. For these head and capacity rotational For these head and capacity rotational speed is 600 rpm specific speed is 9539 runner diameter is 340 mm and runner width is 416 mm.

Cross Flow Turbine Design For Energy Production And Discharge Regulation Journal Of Hydraulic Engineering Vol 141 No 3
About design optimization of cross-flow hydraulic turbines.
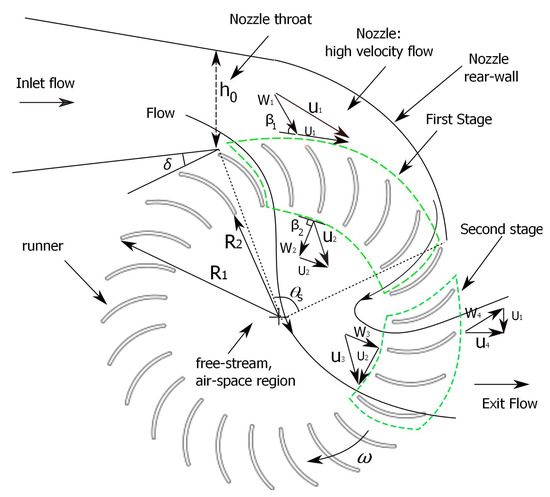
. The following image shows the passage of the water jet through the turbine. It represents the feasible reply to the need of a satisfactory turbine which can be manufactured without the use of a foundry. A cross-flow turbine Bánki-Michell turbine or Ossberger turbine is a water turbine developed by the Australian Anthony Michell the Hungarian Donát Bánki and the German Fritz Ossberger.
Unlike most water turbines which have axial or radial flows in a cross-flow turbine the water. CDB Turbine Design Calculationsxls Spreadsheet of calculations on runner and noozle dimensions and properties. Cross-flow or Banki-Michel turbines are a very efficient and economic choice that allows a very good costbenefit ratio for energy production located at the end of conduits carrying water from a water source to a tank.
Michell obtained patents for his turbine design in 1903 and the manufacturing company Weymouth made it for many years. The two main types of impulse turbine are Pelton and cross-flow turbines. DESIGN OF CROSS FLOW TURBINE Design of turbine is important aspect for any hydropower system and design basics are taken from Mockmore C.
Cross flow turbines also known as vertical-axis turbines capture kinetic energy of moving water with spinning blades oriented perpendicular to the direction of flow. Also a Cross Flow turbine is designed with a gross head of 10 meters and a flow rate of 04 m3s. Water is directed onto the turbine through a nozzle that creates a flat sheet of.
Between 2002 2005 conditions were optimal for many workshops to learn the trade of manufacturing turbines and related equipment. However it should also be noted that designing this kind of a turbine is no childs play. ρ is the density of water 1000kgm3 Q is the flow in m 3s h is the head in m Taking into account the expected head losses in the system as discussed in Section 31 the net head.
Scientific bulletin of thepolytechnic. Of Cross-flow turbine that will generate 100 kW output power from head of 28 m and flow rate of 05 m3s. Added to the design such as an internal manual water flow valve which has made the flow control doors obsolete.
This contribution deals with the design of cross flow water turbines. The mechanical stress sustained by the blades depends on the basic geometrical specifications of the cross flow water turbine its rotational speed the exact geometry of the blades and the velocity of the upstream water current. Water flow through the cross-flow turbine.
The water strikes the. Krishna Nakami Alex Arter Rolf Widmer Markus Eisenring. Power outputs are typically 2KW up to 100KW but small Hydro Systems can be built up to 3 MW.
Cross-flow Turbine The cross-flow water turbine is an efficient and robust flow machine that works under a wide range of head and flow condi-tions. A cross-flow turbine Bánki-Michell turbine or Ossberger turbine is a water turbine developed by the Australian Anthony Michell the Hungarian Donát Bánki and the German Fritz Ossberger. Therefore OSSBERGER Crossflow Turbines operate almost all year round even when other turbine types have long since stopped working.
51 rows Cross Flow Turbine. A water stream hits each bucket on the runner. The PT Pamir Turbine is the most heavy duty cross flow turbine now offered by Remote HydroLight.
THE CROSS-FLOW WATER TURBINE Also called the BankiMitchellOssberger Turbine A Design Manual Metric System The crossflow water turbine is widely considered by many to be the most efficient and apt type of turbine for applications in microhydro and picohydro projects. The mechanical stress sustained by the blades depends on the basic geometrical specifications of the cross flow water turbine its rotational speed the exact geometry of the blades and the velocity of. University of Timisoara Fred Coll Andres Hernandez Nicholas Mohammed 2009.
Ossbergers first patent was granted in 1933 Free Jet. Michell obtained patents for his turbine design in 1903 and the manufacturing company Weymouth made it for many years. Both cells together process full flow.
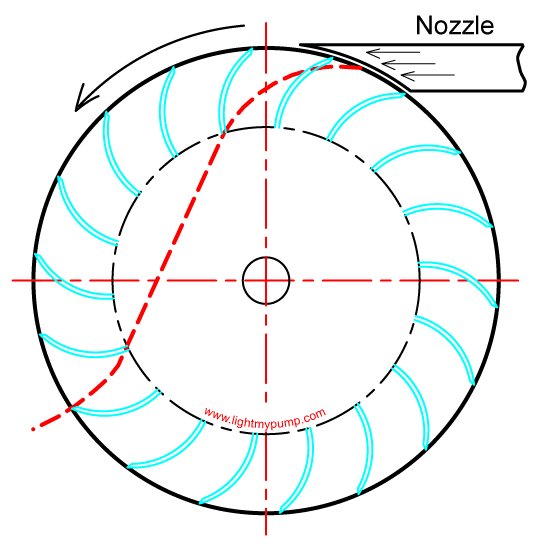
The standard division of the inlet cells is 12. If the water flow is variable then the Crossflow turbine is designed with two cells. The Crossflow Turbine is also known as an Ossberger Turbine and is a good low head high flow turbine even though it is technically an inpulse turbine.
These blades are generally sharpened to increase the efficiency of the turbine by reducing the resistance to water flow. During the operation the blades are. This publication is not simply an additional book on cross flow turbines.
Cross-flow or Banki-Michel turbines are a very efficient and economic choice that allows a very good costbenefit ratio for energy production. Cross flow water turbine design manual Valentines Working day is approaching it is just a month absent but there are a lot of stuff to organize from dresses on the ingesting area from bouquets into the items baskets We have now to rearrange almost everything for our family and friends. This contribution deals with the design of cross flow water turbines.
An impulse turbine is generally suitable for high-head low-flow applications. The narrower cell processes small water flow and the wider cell processes medium flow. The efficiency curve of a cross-flow is roughly flat from half to full flow giving around 60 to 70 of the available stream energy to the turbine shaft across a wide range of flow con-ditions.
With no suction on the down side of the turbine the water flows out the bottom of the turbine housing after hitting the runner. As a result the water flow is used from 100 to 12 with maximum efficiency and the. In the paper the optimum design of a cross-flow turbine is sought after assuming a flow rate variable in time.
Cross Flow Turbine Design Volume 3 Author. H Head m Q Discharge l s N Rotation per minute rpm D1 Outer diameter of the cross flow turbine r1D12 mm. And Merryfield F 1.
The centerline of the water jet is shown as the dashed red line. They can be mounted in either vertical or horizontal orientations. The small unit only requires 5 of the design water volume to start the turbine.
The T12 turbine which is a tested cross. Water flows perpendicular to the devices axis of rotation. This is achieved by two cells inside the turbine which can operate independently of each other.
Applications in microhydro and picohydro projects. Turbine component calculations are adjusted to the application and manual calculations are used to the validation and application testing. A crossflow turbine is designed using a large cylindrical mechanism composed of a central rotor surrounded by a cage of blades arranged into a water wheel shape.
A Design Manual Metric System The crossflow water turbine is widely considered by many to be the most efficient and apt type of turbine for.

Cross Flow Turbine Design Volume 3 Skat Consulting

Pdf Design And Analysis Of Cross Flow Turbine For Micro Hydro Power Application Using Sewerage Water Semantic Scholar

Pdf Cross Flow Turbine Design For Variable Operating Conditions Semantic Scholar

Energies Free Full Text The Design Of High Efficiency Crossflow Hydro Turbines A Review And Extension Html
Design And Calculations For The Cross Flow Turbine



0 comments
Post a Comment